Introduction To Gaming PC Components
Whether you’re a beginner or a veteran, the process of learning to build a gaming PC is enjoyable yet arduous. A solid grasp of gaming PC parts is needed to ensure an even, effective, and powerful build. Of all components, the most important are the CPU (Central Processing Unit) which processes tasks and executes commands, and the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) that renders graphics and images to ensure high-quality gameplay. These two will clear the essential need for data regarding each component to forge an educated journey toward ultimate building success in 2025.
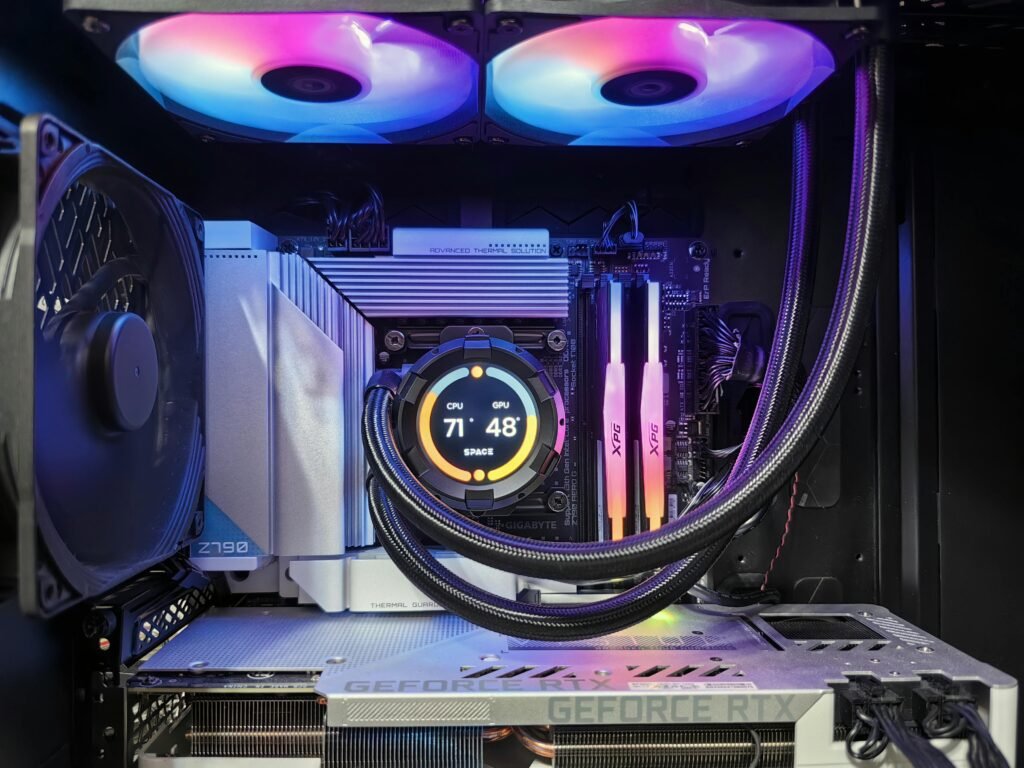

Table of Contents
The component that serves as the center of the computer is the motherboard, as it connects all components and allows for communication between them. The motherboard also determines what CPUs, RAM, etc. can be implemented in the system. Another key component is random access memory (RAM), which acts as short-term memory that the CPU can access. Increased RAM means that the computer does not freeze or slow down when multitasking because there’s more memory available for temporary file storage.
The component that supplies power to everything is the power supply unit (PSU); getting a good PSU that offers enough power is important because without it, no other component will even turn on. For storage, the components can be solid state drives (SSD) or hard disk drives (HDD); SSDs have faster read/write speeds meaning data access is faster—leading to a more responsive experience—while HDDs tend to be less expensive for larger storage sizes.
Overall, knowing about these components aids in the decision-making process for implementing a well-balanced and efficient PC.
Understanding the Central Processing Unit (CPU): Unlocking Incredible Performance & Avoiding Common Pitfalls
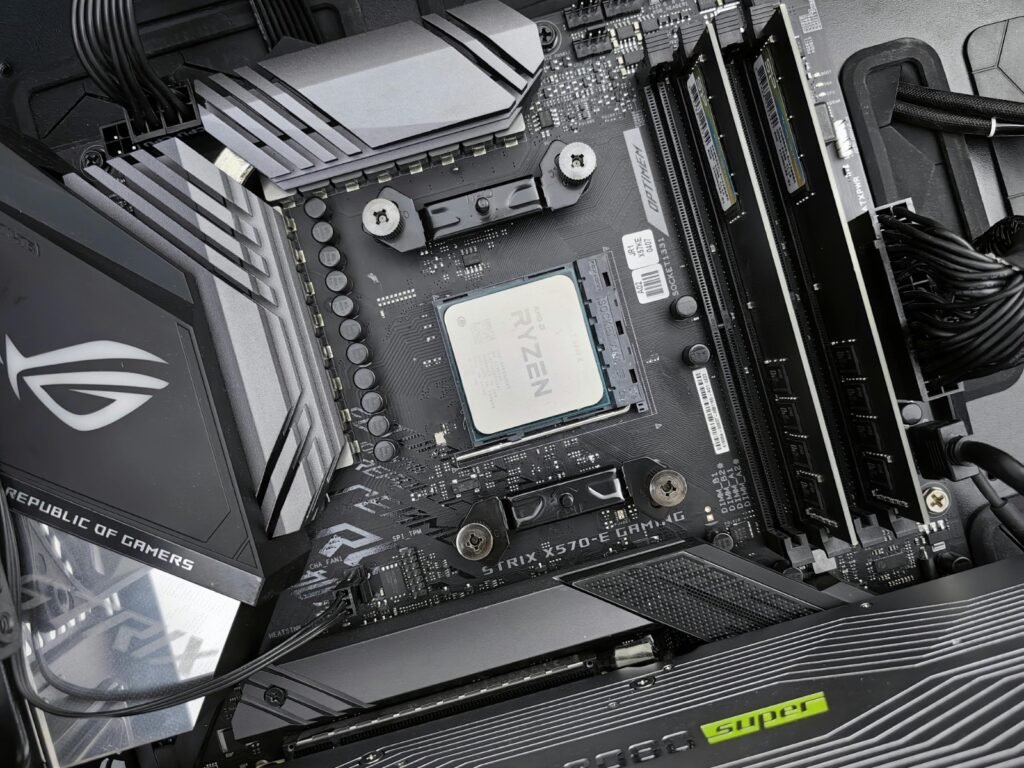

The Central Processing Unit (CPU), often called the computer’s brain, orchestrates all instructions, powering exceptional system performance. A robust CPU delivers lightning-fast processing, seamless multitasking, and flawless performance for intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, and complex data analysis. When selecting a CPU, prioritize key factors such as core count, clock speed, and motherboard compatibility to match your needs. Leading brands like Intel and AMD provide diverse options, from cost-effective processors to cutting-edge, high-performance models. Choosing the right CPU guarantees a smooth, responsive, and highly efficient computing experience tailored to your goals.
Graphics Cards Explained for Beginners: How to Choose the Right GPU and Avoid Common Mistakes
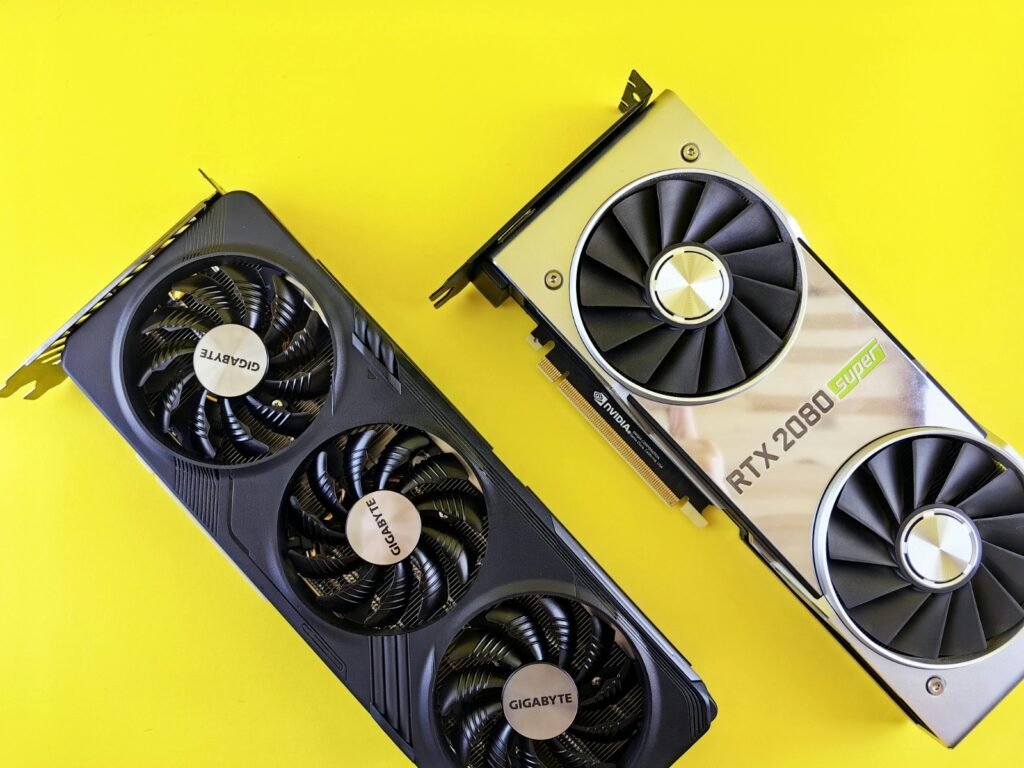

A graphics card (GPU) is a critical component for rendering images, videos, and games with high performance and visual clarity. Dedicated GPUs, unlike integrated graphics, have their own memory (VRAM) and processing power, making them essential for gaming, video editing, 3D rendering, and AI workloads. Choosing the right GPU depends on factors like performance needs, resolution, refresh rate, and budget. Trusted brands like NVIDIA and AMD offer a range of options, from entry-level to high-end models, ensuring smooth performance for various tasks. Proper cooling and power supply compatibility are also key considerations for optimal GPU performance.
The Role of the Motherboard: Empowering System Performance & Preventing Compatibility Nightmares
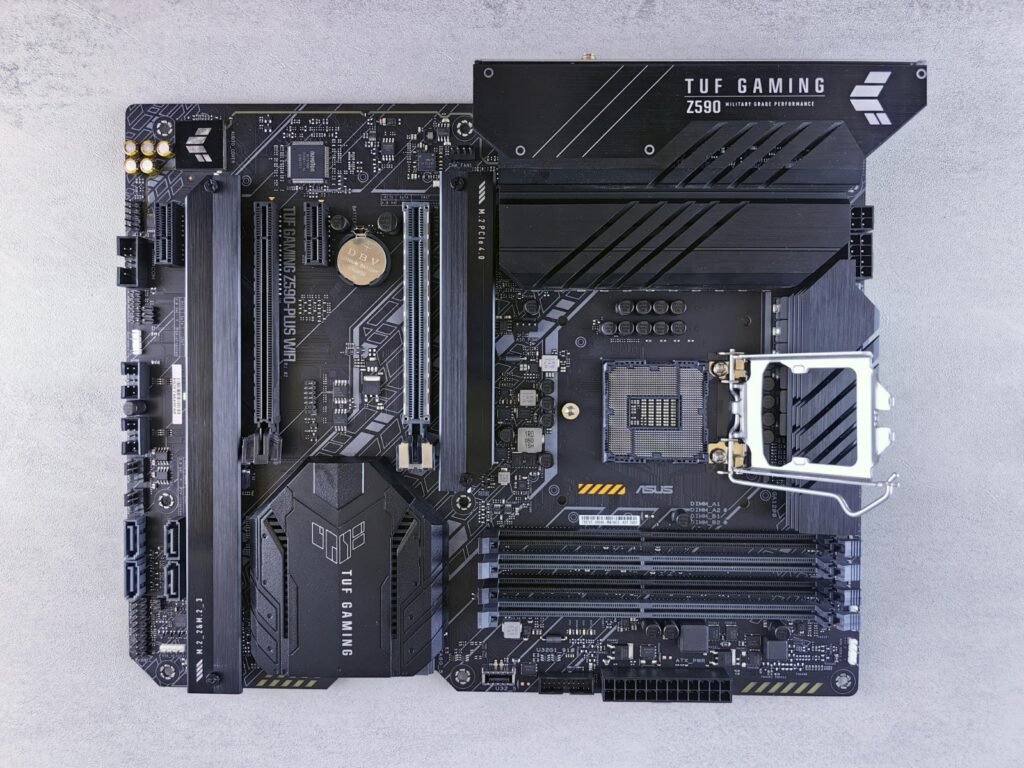

The motherboard is the backbone of any computer, connecting all essential components and ensuring smooth communication between them. It houses the CPU, RAM, GPU, and storage devices while providing expansion slots for future upgrades. A quality motherboard ensures stability, efficient power distribution, and support for high-speed connectivity, including USB, Wi-Fi, and PCIe slots. Choosing a motherboard that matches your processor, supports your desired features, and comes from a trusted brand is crucial for long-term reliability and performance.
RAM: The Key to Unlocking Maximum Performance – Speed Up Your System & Prevent Critical Bottlenecks in 2025
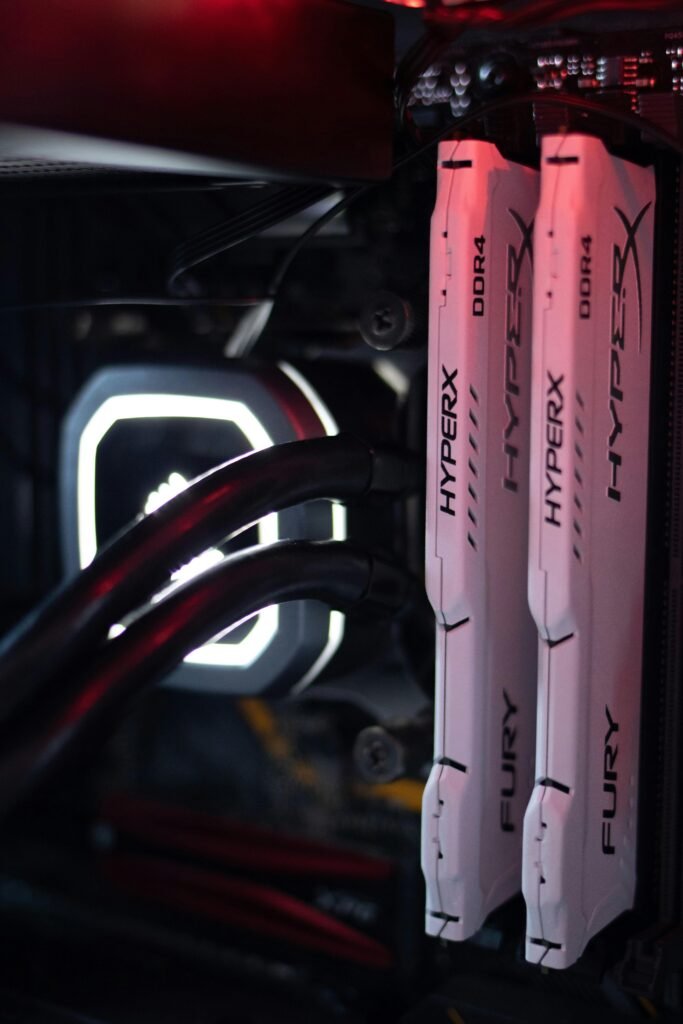

RAM (Random Access Memory) is a vital component that directly impacts your system’s speed and multitasking capabilities. It temporarily stores active data, allowing the processor to access information quickly for smooth performance. More RAM enables seamless multitasking, faster load times, and improved responsiveness in demanding applications like gaming and video editing. Choosing high-speed, low-latency RAM from a reputable brand ensures reliability and compatibility with your system. For optimal performance, it’s important to balance capacity and speed based on your specific needs.
Choosing the Right Power Supply Unit (PSU): Maximize Efficiency & Avoid Costly Power Failures
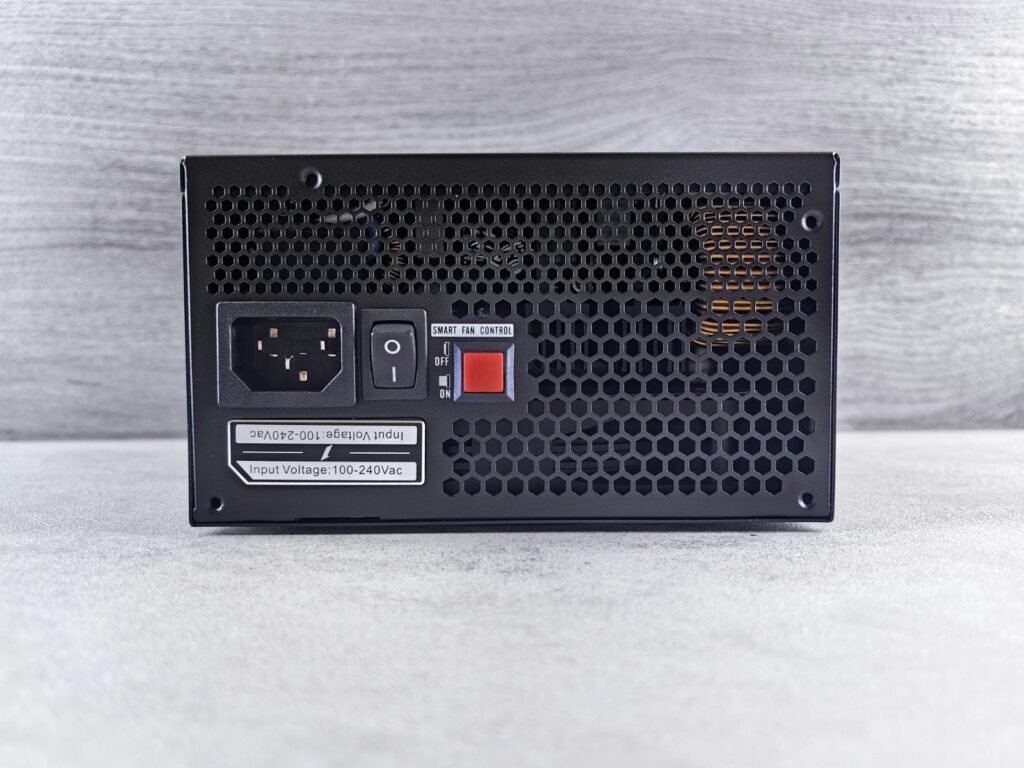

Choosing the right Power Supply Unit (PSU) is crucial for system stability and efficiency. A PSU should provide sufficient wattage to support all components, with some headroom for future upgrades. Opting for an 80 Plus certified unit ensures better energy efficiency and reliability, with Gold or higher ratings offering the best balance of performance and power savings. Modular PSUs help with cable management, improving airflow inside the case. It’s also essential to choose a PSU from a reputable brand to ensure quality, longevity, and protection against power surges.
SSD vs. HDD: Understanding Storage Options to Boost Performance & Avoid Sluggish Load Times
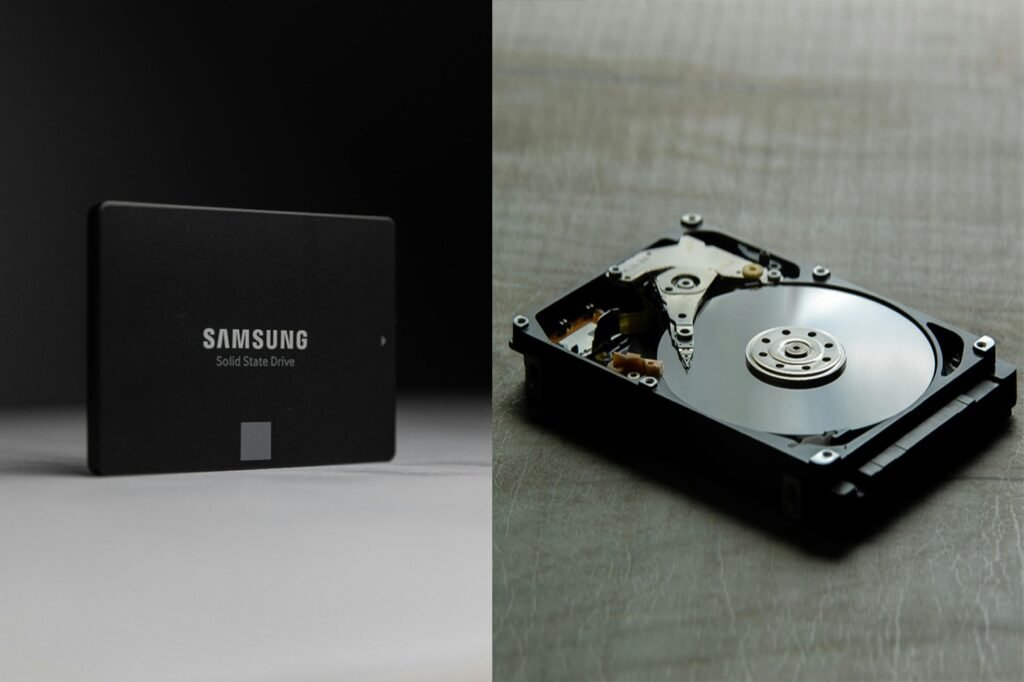
When choosing between an SSD (Solid State Drive) and an HDD (Hard Disk Drive), it’s essential to consider speed, durability, and cost. SSDs use flash memory, offering significantly faster read/write speeds, making them ideal for gaming, multitasking, and quick system boot-ups. They are also more durable since they lack moving parts. In contrast, HDDs are more affordable and provide larger storage capacities, making them suitable for storing large files and backups. While SSDs are the preferred choice for performance, HDDs remain a budget-friendly option for bulk storage needs.
Cooling Solutions for Peak Performance: Enhance Efficiency & Prevent Dangerous Overheating
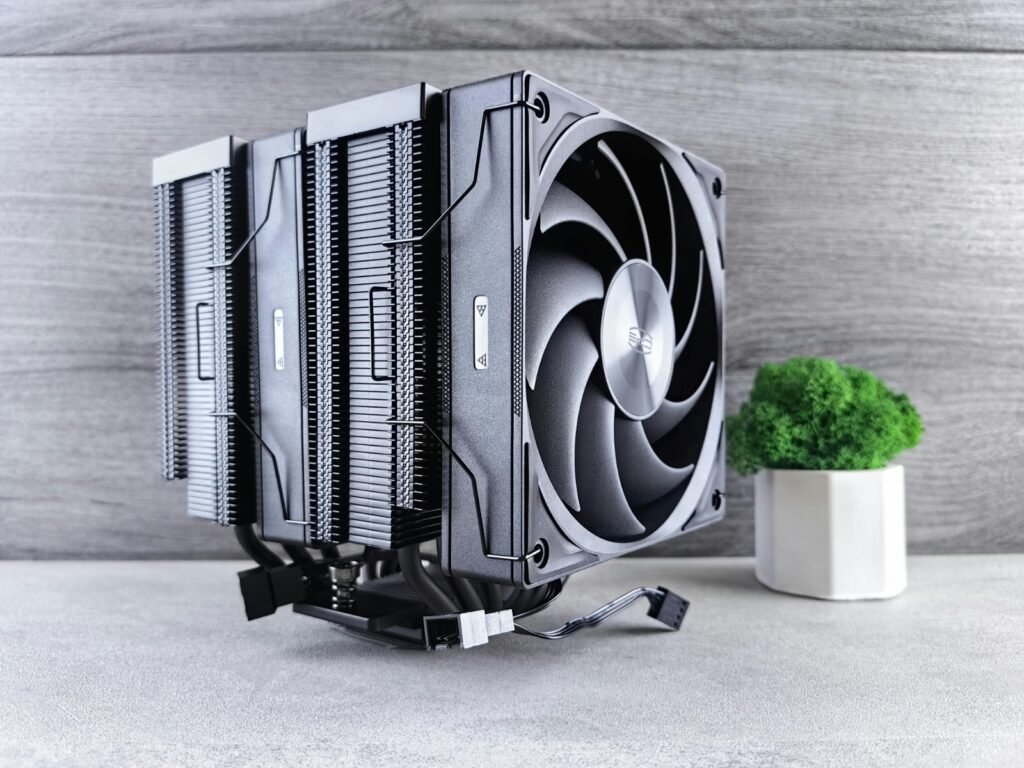

Effective cooling solutions are essential for maintaining optimal system performance and longevity. Air coolers, like the Cooler Master Hyper 212 and DeepCool GAMMAXX 400, offer budget-friendly reliability, while AIO liquid coolers provide superior thermal management for high-performance builds. Proper airflow, quality thermal paste, and efficient case ventilation further enhance cooling efficiency.
Best Gaming PC Build for Ultra Gamers in 2025
Processor (CPU) – Intel Core i9-14900K or AMD Ryzen 9 9900X
- Pros & Cons: Processor (CPU) – Intel Core i9-14900K or AMD Ryzen 9 9900X
- Intel Core i9-14900K
- Pros: Higher clock speeds, great for gaming, strong single-core performance.
- Cons: Higher power consumption, runs hot.
- AMD Ryzen 9 9900X
- Pros: Better efficiency, strong multi-core performance, great for productivity.
- Cons: Slightly lower gaming performance than Intel, depends on fast RAM.
Graphics Card (GPU) – NVIDIA RTX 5090 or AMD Radeon RX 7800 XT
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5090
Specifications:
- Architecture: Blackwell
- CUDA Cores: 21,760
- Memory: 32 GB GDDR7
- Memory Bus: 512-bit
- TDP: 575W
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5090 – Pros & Cons
- Pros (Advantages):
- Extreme Performance
- Next-gen Blackwell Architecture – Huge performance boost over RTX 4090
- Massive CUDA Core Count (21,760 cores) – Faster rendering & AI processing
- High Boost Clock Speeds (2,410 MHz) – Smoother gameplay in demanding titles
- Ultimate 4K & 8K Gaming
- Perfect for 4K Ultra Gaming – Runs most games at 100+ FPS
- DLSS 4 with AI Frame Generation – Higher frame rates with AI assistance
- 8K Support – Great for ultra-high resolution gaming & content creation
- AI & Content Creation Ready
- 32GB GDDR7 VRAM – Ideal for video editing, 3D rendering, and AI workloads
- Ray Tracing Enhancements – More realistic lighting & reflections
- AV1 Encoding & High-End Streaming – Better quality for content creators
- Future-Proofing
- PCIe 5.0 Support – Faster data transfer speeds
- HDMI 2.1 & DisplayPort 2.1 – Supports high refresh rate 4K & 8K displays
- Longer Lifespan – Expected to remain powerful for years
- Cons (Disadvantages):
- High Power Consumption
- 575W TDP – Requires a high-wattage PSU (1200W+ recommended)
- Generates significant heat – Needs advanced cooling solutions
- Expensive Pricing
- Premium price tag (~$2000+) – Not budget-friendly
- May have limited availability at launch – Potential scalping issues
AMD Radeon RX 7800 XT
Specifications:
- GPU Architecture: AMD RDNA 3
- Compute Units (CUs): 60
- Ray Accelerators: 60
- Stream Processors: 3,840
- Boost Clock: Up to 2,430 MHz
- Base Clock: 1,295 MHz
- VRAM (Memory): 16GB GDDR6
- Memory Bus: 256-bit
- Memory Bandwidth: 624 GB/s
- Infinity Cache: 64MB
- TDP (Power Draw): 263W
- PCIe Interface: PCIe 4.0 x16
- Display Outputs: 2x DisplayPort 2.1, 1x HDMI 2.1
- Recommended PSU: 700W+
- AMD Radeon RX 7800 XT Pros & Cons
- Pros:
- Great 1440p performance (Can handle 4K with tweaks)
- 16GB VRAM (More future-proof than RTX 4070)
- Strong price-to-performance ratio
- Supports FSR 3 for FPS boost
- Better value than NVIDIA RTX 4070
- Cons:
- Ray tracing performance is weaker than NVIDIA
- No DLSS (Only FSR is available)
- Power consumption is slightly higher (263W TDP)
Motherboard – ASUS ROG Maximus Z790 Hero (Intel) / MSI MEG X670E GODLIKE (AMD)
ASUS ROG Maximus Z790 Hero (Intel)
Best for: Intel 12th, 13th, and 14th Gen CPUs (i7-14700K, i9-14900K, etc.)
- Pros: High-end VRMs, PCIe 5.0, WiFi 6E, Thunderbolt 4, great overclocking, premium build, AI features.
- Cons: Expensive, overkill for casual users, limited PCIe 5.0 lanes, high power draw.
MSI MEG X670E GODLIKE (AMD)
Best for: Ryzen 7000 series (7950X3D, 7800X3D, etc.)
- Pros: Top-tier VRMs, PCIe 5.0, WiFi 6E, USB4, excellent overclocking, premium build, large touchscreen display.
- Cons: Extremely expensive, very large (E-ATX), overkill for most users, high power consumption.
RAM – 32GB DDR5 (6000MHz or higher)
Best Overall:
- G.Skill Trident Z5 RGB DDR5-7200 CL34 – High speed, tight timings, stylish RGB, great for Intel.
Best for AMD:
- Corsair Dominator Platinum RGB DDR5-6000 CL30 – Optimized for Ryzen 7000, low latency, premium build.
Best High-Performance:
- Kingston Fury Renegade DDR5-8000 CL38 – Extreme speeds, excellent for Intel 14th Gen, efficient cooling.
Storage – 2TB NVMe Gen 5 SSD (Samsung 990 Pro or WD Black SN850X)
1. Samsung 990 Pro
- Read Speed: 7,450 MB/s
- Write Speed: 6,900 MB/s
- Controller: Samsung in-house (8nm)
- NAND Type: TLC (3D V-NAND)
- Cache: 2GB LPDDR4
- Endurance: 1,200 TBW
- Power Efficiency: Lower power draw (good for laptops & desktops)
- Software: Samsung Magician
- Optional Heatsink Version: Yes
- Best for:
- Gaming (Quick load times)
- High-performance applications
- Power-efficient builds (Lower power draw)
2. WD Black SN850X (2TB)
- Read Speed: 7,300 MB/s
- Write Speed: 6,600 MB/s
- Controller: WD in-house
- NAND Type: TLC (BiCS5 3D NAND)
- Cache: DRAM cache
- Endurance: 1,200 TBW
- Game Mode 2.0: Optimized for DirectStorage (faster game loading)
- Software: WD Dashboard
- Optional Heatsink Version: Yes
- Best for:
- Gaming & DirectStorage (Great for future games)
- High-speed file transfers & editing
- Great thermal performance (especially with a heatsink)
Power Supply (PSU) – 1000W 80 Plus Platinum
- A 1000W 80 Plus Platinum power supply is a high-efficiency PSU designed for high-end gaming, workstation, or overclocking builds. Here’s what you need to know:
- Best Use Cases
- High-end gaming PCs (RTX 4090, RX 7900 XTX, etc.)
- Overclocked CPUs & GPUs
- Workstations with multiple NVMe SSDs, HDDs, and peripherals
- Future-proofing for next-gen hardware
- Popular 1000W 80 Plus Platinum PSU Models
- Corsair RM1000x Shift (ATX 3.0, Fully Modular)
- Key Features
- Wattage: 1000W, suitable for high-end systems.
- Efficiency: 80 PLUS Gold certified, offering up to 90% efficiency and lower power consumption.
- Modular Design: Fully modular with Corsair Type 5 micro-fit connectors, allowing you to use only the cables you need for a cleaner build.
- Side Cable Interface: Innovative side-mounted connectors improve cable management and accessibility, especially in cases with PSU shrouds.
- Cooling: 140mm fluid dynamic bearing fan with Zero RPM mode ensures quiet operation under low to medium loads.
- ATX 3.0 & PCIe 5.0 Compliance: Supports the latest standards, including a 12VHPWR connector for next-gen GPUs.
- Warranty: Backed by a 10-year warranty, reflecting Corsair’s confidence in its durability.
- Seasonic PRIME TX-1000 (High-end, silent fan, ultra-durable)
- The Seasonic PRIME TX-1000 is a premium 1000W 80 PLUS Titanium-certified PSU offering up to 94% efficiency. It features a fully modular design, a 135mm fluid dynamic bearing fan with hybrid silent mode, and high-quality Japanese capacitors. With a 12-year warranty, it’s ideal for high-performance, quiet PC builds.
- MSI MAG A750GL PCIE5 (Compact, great efficiency)
- The MSI MAG A750GL PCIE5 is a 750W 80 Plus Gold certified power supply featuring ATX 3.0 and PCIe 5.0 support, a fully modular design, Japanese capacitors, and a quiet 120mm FDB fan—delivering stable, efficient, and future-ready performance trusted by PC enthusiasts.
- MSI MEG Ai1000P PCIe 5.0 (12VHPWR ready, excellent cooling)
- The MSI MEG Ai1000P PCIe 5.0 is a 1000W, 80 PLUS Platinum-certified PSU featuring a fully modular design, native 12VHPWR connector for up to 600W GPU power, and ATX 3.0 compliance. It includes a 120mm hydro-dynamic bearing fan, semi-passive cooling, and supports MSI’s Gaming Intelligence software for monitoring and control.
Cooling System – Corsair iCUE H150i Elite LCD XT (AIO Liquid Cooler)
- Performance Benefits:
- Excellent cooling for overclocked and high-performance CPUs.
- RGB and LCD screen for aesthetics and system monitoring.
- Quiet operation, even under load.
- Pros & Cons
- Pros:
- LCD customization options.
- Great cooling efficiency.
- Quiet and efficient fans.
- Easy to install.
- Cons:
- Expensive compared to non-LCD AIO coolers.
- Requires iCUE software for full customization.
- Large size (360mm) may not fit in all cases.
Cabinet (Case) – Lian Li O11 Dynamic EVO XL
- Pros & Cons:
- Exceptional Build Quality: Utilizes high-quality materials, offering a sturdy and premium feel.
- Versatile Layout: The reversible design allows users to customize the case orientation to their preference, enhancing display options.
- Ample Cooling Support: Capable of housing extensive cooling solutions, including multiple large radiators and fans, making it ideal for advanced air or liquid cooling setups.
- Spacious Interior: Offers generous space for high-end components, facilitating complex builds and efficient cable management.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The combination of tempered glass panels and customizable RGB lighting enhances the visual appeal of the build.
- Cons:
- Large Footprint: Due to its full-tower size, it requires substantial desk or floor space, which may not be suitable for all environments.
- Premium Price Point: The high-quality materials and features come at a higher cost compared to mid-range cases.
- Complex Assembly: The extensive modularity and customization options may lead to a more involved and time-consuming assembly process, especially for novice builders.
Monitor – LG Electronics Ultragear 21:9 Curved Gaming LED Monitor
LG Electronics Ultragear
The LG UltraGear 34″ 21:9 Curved Gaming Monitor offers a 3440×1440 QHD resolution, 160Hz refresh rate, 1ms response time, HDR10 support, and AMD FreeSync Premium, delivering immersive ultrawide visuals and smooth performance.
- Pros & Cons
- Pros:
- Immersive 21:9 curved QHD display – Great for gaming and multitasking
- 160Hz refresh rate & 1ms response time – Smooth, fast performance
- AMD FreeSync Premium & NVIDIA G-SYNC Compatible – Tear-free gameplay
- HDR10 support – Enhanced colors and contrast
- Ergonomic stand – Adjustable height, tilt, and swivel
- Cons:
- High price point – Premium features come at a cost
- Large footprint – Needs ample desk space
- No built-in speakers – External audio required
- Limited HDR brightness – Not as vibrant as true HDR displays
Final Thoughts
This build is best for 4K Ultra gaming, streaming and content creation. If your budget is a little low, then RTX 5080 + Ryzen 7 7800X3D can also be a good option.
Budget Gaming PC Build 2025 ($817 – $1,168)
Processor (CPU) – AMD Ryzen 5 7600X or Intel Core i5-13600KF
Gaming and multitasking For best performance at budget.
Pros & Cons: AMD Ryzen 5 7600X & Intel Core i5-13600KF
AMD Ryzen 5 7600X
The AMD Ryzen 5 7600X is a 6-core, 12-thread processor built on Zen 4 architecture, delivering excellent gaming and productivity performance. With boost clocks up to 5.3GHz, DDR5 and PCIe 5.0 support, it’s a trusted choice for high-efficiency, mid-range builds.
- Pros: Strong single-core performance, PCIe 5.0 & DDR5 support, power-efficient.
- Cons: Requires AM5 motherboard, no integrated graphics, higher platform cost.
Intel Core i5-13600KF
The Intel Core i5-13600KF is a 13th Gen Raptor Lake processor featuring 14 cores (6 Performance + 8 Efficient) and 20 threads. It offers a base clock of 3.5 GHz and a max turbo frequency of 5.1 GHz, with 24MB of Intel Smart Cache. This unlocked CPU supports DDR5 memory, PCIe 5.0, and requires discrete graphics. It’s ideal for gaming and multitasking, delivering high performance at a competitive price.
- Pros: Excellent multi-core performance, great for gaming & productivity, DDR4/DDR5 support.
- Cons: Higher power consumption, no integrated graphics, requires good cooling.
Graphics Card (GPU) – NVIDIA RTX 4060 Ti (8GB) or AMD RX 7700 XT
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 Ti (8GB) Key Features:
- Architecture: Ada Lovelace (AD106)
- CUDA Cores: 4,352
- Base Clock Speed: 2,310 MHz
- Boost Clock Speed: Up to 2,535 MHz
- Memory: 8 GB GDDR6
- Memory Interface: 128-bit
- Memory Bandwidth: 288 GB/s
- Ray Tracing Cores: 3rd Generation
- Tensor Cores: 4th Generation
- TDP: 160W
- Recommended System Power: 550W
- Power Connector: 1x 16-pin
- Pros:
- Efficient 1080p Performance: Delivers high frame rates in 1080p gaming scenarios.
- Advanced Features: Supports NVIDIA’s DLSS 3 and Reflex technologies, enhancing gaming performance and responsiveness.
- Power Efficiency: Offers low power consumption, making it suitable for systems with limited power capacity.
- Cons:
- Limited Memory Capacity: The 8GB VRAM may be insufficient for some modern games at higher settings, potentially leading to performance issues.
- Narrow Memory Bus: The 128-bit memory interface can constrain memory bandwidth, affecting performance in memory-intensive applications.
- Modest Performance Uplift: Offers limited performance improvement over its predecessor, the RTX 3060 Ti, raising concerns about its value proposition.
AMD Radeon RX 7700 XT Key Features:
- Architecture: RDNA 3 (Navi 32)
- Compute Units: 54
- Stream Processors: 3,456
- Game Clock Speed: 2,171 MHz
- Boost Clock Speed: Up to 2,544 MHz
- Memory: 12 GB GDDR6
- Memory Interface: 192-bit
- Memory Bandwidth: 432 GB/s
- Infinity Cache: 48 MB
- Ray Accelerators: 54
- TDP: 245W
- Recommended System Power: 600W
- Power Connectors: 2x 8-pin
- Pros:
- Robust 1440p Performance: Capable of delivering high frame rates at 1440p resolution, catering to gamers seeking detailed visuals.
- Generous VRAM: Equipped with 12GB of GDDR6 memory, providing better support for high-resolution textures and future-proofing.
- Competitive Pricing: Offers a cost-effective alternative to higher-priced GPUs with similar performance levels.
- Cons:
- High Power Consumption: The 245W TDP necessitates robust cooling solutions and a quality power supply.
- Performance Overlap: Close in price to the RX 7800 XT, which offers better performance, potentially diminishing the 7700 XT’s value proposition.
- Limited Availability: Depending on the region, availability may be constrained, affecting pricing and accessibility.
Motherboard – B650 Tomahawk WiFi (AMD) / MSI PRO Z690-A WiFi (Intel)
Pros & Cons: MSI B650 Tomahawk WiFi (AMD) & MSI PRO Z690-A WiFi (Intel)
MSI B650 Tomahawk WiFi (AMD)
The MSI MAG B650 Tomahawk WiFi is a reliable AM5 ATX motherboard supporting AMD Ryzen 7000 series CPUs. It features DDR5 support, PCIe 4.0 slots, Wi-Fi 6E, and robust 14+2 phase VRMs with Core Boost technology. Ideal for gamers seeking performance and stability.
- Pros: Solid VRMs, PCIe 4.0, WiFi 6E, great value, good cooling.
- Cons: No PCIe 5.0 GPU slot, fewer USB ports.
MSI PRO Z690-A WiFi (Intel)
The MSI PRO Z690-A WiFi is a reliable ATX motherboard for Intel 12th–14th Gen CPUs, supporting DDR5 RAM up to 6400+ MHz (OC). It features PCIe 5.0, 4x M.2 slots with Shield Frozr, Wi-Fi 6E, 2.5G LAN, and USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 Type-C. Ideal for high-performance builds.
- Pros: PCIe 5.0, WiFi 6E, good VRMs, DDR4 & DDR5 versions, affordable.
- Cons: No integrated RGB, basic audio, fewer premium features.
RAM – 16GB DDR5 (6000MHz) or DDR4 (3200MHz)
Pros & Cons: G.Skill Trident Z5 RGB 16GB & Corsair Vengeance LPX 16GB
DDR5 – G.Skill Trident Z5 RGB 16GB (6000MHz, CL30)
The G.Skill Trident Z5 RGB 16GB DDR5-6000 CL30 is a high-performance memory module featuring low latency and sleek design. It supports Intel XMP 3.0 for easy overclocking and is ideal for enthusiasts seeking reliable speed and aesthetics.
- Pros: High speed, low latency, great for gaming, stylish RGB.
- Cons: More expensive, requires DDR5-compatible motherboard.
DDR4 – Corsair Vengeance LPX 16GB (3200MHz, CL16)
The Corsair Vengeance LPX 16GB (2x8GB) DDR4-3200 CL16 is a reliable, low-profile memory kit designed for high-performance overclocking. Featuring an aluminum heat spreader for efficient heat dissipation and XMP 2.0 support for easy setup, it’s ideal for gaming and productivity builds.
- Pros: Reliable, affordable, widely compatible.
- Cons: Slower than DDR5, aging technology.
Verdict: DDR5 is the better choice for future-proofing and high-performance Gaming and multitasking will run smoothly DDR4 is also good if budget is too tight.
Storage – 1TB NVMe SSD (Gen 4, Crucial P3 Plus or WD SN770)
Pros & Cons: Crucial P3 Plus (1TB, Gen 4) WD Black SN770 (1TB, Gen 4)
Crucial P3 Plus (1TB, Gen 4)
The Crucial P3 Plus 1TB Gen 4 NVMe SSD offers up to 5000MB/s read speeds, ensuring fast performance for gaming and productivity. It’s a reliable, cost-effective choice for PCIe 4.0 systems, backed by Crucial’s trusted quality and a 5-year warranty.
- Pros: Affordable, decent speeds (5000MB/s), good for gaming.
- Cons: Slower than high-end Gen 4 SSDs, lacks DRAM.
WD Black SN770 (1TB, Gen 4)
The WD Black SN770 1TB Gen 4 NVMe SSD offers reliable performance with read speeds up to 5,150 MB/s and write speeds up to 4,900 MB/s. It’s a cost-effective choice for gamers and professionals seeking fast load times and efficient multitasking.
- Pros: Faster speeds (5150MB/s), reliable, good efficiency.
- Cons: No DRAM cache, not the fastest Gen 4 option.
Verdict: WD SN770 is slightly better in speed and efficiency, while Crucial P3 Plus offers good value.
Power Supply (PSU) – 650W – 750W 80 Plus Bronze/Gold (Deep cool, Corsair, MSI)
Pros & Cons: 80 Plus Bronze/Gold (Deep cool, Corsair, MSI)
80 Plus Bronze
80 Plus Bronze certified PSUs offer reliable efficiency of at least 82% under typical loads. They provide stable power, reduce heat, and are trusted for budget to mid-range systems. Known for solid performance and energy savings without breaking the bank.
- Pros: Affordable, decent efficiency (82-85%), good for budget builds.
- Cons: Less efficient, more heat, not ideal for high-power systems.
80 Plus Gold
80 Plus Gold PSUs deliver trusted efficiency of 87–90%, ensuring stable power, lower heat, and quieter operation. Ideal for gaming and professional builds, they offer reliable performance, energy savings, and long-term durability from respected brands.
- Pros: Higher efficiency (87-90%), less heat, better reliability, great for gaming rigs.
- Cons: More expensive, overkill for low-power builds.
Verdict: Gold is better for long-term efficiency and performance.
Other Best Budget PSU
Cooler Master PSU
The Cooler Master MWE 550 V3 Bronze is a 550W non-modular power supply featuring ATX 3.1 support, 80 Plus Bronze efficiency, a quiet HDB fan, and a 5-year warranty.
- Pros: Efficient (80 Plus Bronze), ATX 3.1 ready, quiet HDB fan, stable power, 5-year warranty.
- Cons: Non-modular cables, limited for high-end builds, basic design.
Corsair PSU
Corsair PSUs are known for high reliability, efficiency (80 Plus Bronze to Titanium), and silent operation. They suit all build levels, from entry to enthusiast. Popular lines include CX, RM, RMx, and AXi, offering modular cables and long warranties.
- Pros: High-quality components, reliable, great efficiency (Gold & Platinum models).
- Cons: Premium models are pricey.
MSI PSU
MSI PSUs deliver stable power with 80 Plus certification, quiet cooling, and sleek design. Suitable for gaming and high-performance builds, popular models like the MPG and MAG series offer modular cables, high-quality components, and reliable protection features.
- Pros: Solid efficiency, good for gaming builds, stylish design.
- Cons: Limited models, higher price than competitors.
Cooling System – Cooler Master Hyper 212 Black Vetroo V5 and DeepCool GAMMAXX 400
Pros & Cons: Cooler Master Hyper 212 Black Vetroo V5 and DeepCool GAMMAXX 400
Cooler Master Hyper 212 Black
- Pros: Affordable, good cooling for mid-range CPUs, quiet operation, sleek black design.
- Cons: Not ideal for high-end overclocking, can be tricky to install, bulkier than some air coolers.
Vetroo V5
- Pros: Affordable, good cooling performance, stylish RGB, compatible with most CPUs.
- Cons: Louder at high speeds, not ideal for heavy overclocking.
Cooler Master Hyper 212
- Pros: Great cooling, quiet fan, solid build, affordable, wide socket compatibility.
- Cons: Bulky size, no RGB (basic models), may block tall RAM.
Cabinet (Case) – Ant Esports ICE 511 MT or Lian Li Lancool 215
With good airflow and RGB looks.
Pros Cons: Ant Esports ICE 511 MT \ Lian Li Lancool 215
Ant Esports ICE 511 MT
- Pros: Affordable, good airflow, mesh front panel, RGB fans included.
- Cons: Basic build quality, limited cable management, fewer premium features.
Lian Li Lancool 215
- Pros: Excellent airflow, solid build quality, spacious interior, dual 200mm ARGB fans.
- Cons: Slightly pricier, limited front I/O ports.
Verdict: Lancool 215 offers better quality and cooling, while ICE 511 MT is a budget-friendly option.
Monitor – 24-inch, 165Hz, 1ms IPS Panel (Acer Nitro VG240YS or Gigabyte G24F 2) For smooth FPS and fast response time.
Pros & Cons: Acer Nitro VG240YS or Gigabyte G24F 2\ Gigabyte G24F 2
Acer Nitro VG240YS
- Pros: 165Hz refresh rate, good color accuracy, budget-friendly, decent build quality.
- Cons: No height adjustment, average HDR, slower response time than competitors.
Gigabyte G24F 2
- Pros: 180Hz refresh rate, better response time, good color accuracy, ergonomic stand.
- Cons: Slightly more expensive, HDR performance is mediocre.
Verdict: G24F 2 is better for competitive gaming, while VG240YS is a solid budget option.
Final Thoughts
This is the best budget gaming PC that can easily run games like GTA 6, Cyberpunk 2077, Call of Duty, Valorant, RDR2 at 1080p/1440p on High settings.
If the budget is low (~$583 – $700) then RTX 4060 + Ryzen 5 5600 will be the best combo.
It will be easy to upgrade GPU and RAM in the future.
Conclusion
If you are looking for a budget gaming PC build that can handle 1080p or 1440p gaming smoothly, then Ryzen 5 7600X + RTX 4060 Ti or i5-13600KF + RX 7700 XT are the best value-for-money combos. These builds provide fast performance, smooth gameplay and future upgrade options. If the budget is low (~$583 – $700) then Ryzen 5 5600 + RTX 4060 is also a good option. It will be easy to upgrade GPU and RAM in the future. There can be some tweaks as per your budget and gaming preference,

The website design looks great—clean, user-friendly, and visually appealing! It definitely has the potential to attract more visitors. Maybe adding even more engaging content (like interactive posts, videos, or expert insights) could take it to the next level. Keep up the good work!
The motherboard is indeed the backbone of any computer, connecting all vital components seamlessly. RAM plays a crucial role in multitasking, ensuring smooth performance without lags. A reliable PSU is essential to keep everything powered and functioning correctly. SSDs and HDDs each have their advantages, with SSDs offering speed and HDDs providing cost-effective storage. How do you decide which storage option suits your needs best?
hi
The motherboard is indeed the backbone of any computer, ensuring all components work in harmony. RAM plays a crucial role in multitasking, preventing the system from slowing down. A reliable PSU is essential, as it powers every part of the computer. SSDs provide faster data access, enhancing overall performance, while HDDs offer more storage at a lower cost. How do you decide which storage option best suits your needs?
The explanation of computer components is quite comprehensive and helpful for someone looking to build or upgrade their PC. I found the details about the motherboard and its role in connecting all parts particularly interesting—it’s amazing how one component can be so central to functionality. The comparison between SSDs and HDDs was also enlightening, especially the trade-off between speed and cost. However, I wonder if there’s a scenario where using both an SSD and an HDD in the same system would be ideal—like having the OS on the SSD and storing large files on the HDD. What’s your take on that? Additionally, while the CPU’s importance is clear, do you think the average user could overestimate the need for a high-end CPU when a mid-range one would suffice? Lastly, I’d love to hear your thoughts on how future advancements might change the way we look at these components—say, if storage or processing technologies evolve drastically. What do you think?
The motherboard is indeed the backbone of any computer, connecting all the essential components. It’s fascinating how the choice of motherboard dictates the compatibility of CPUs and RAM, ultimately shaping the system’s capabilities. RAM plays a crucial role in multitasking, and I agree that increasing it can significantly enhance performance. The power supply unit (PSU) often gets overlooked, but it’s vital to ensure stability and longevity of the system. When it comes to storage, SSDs are a game-changer with their speed, though HDDs still have their place for bulk storage on a budget. The CPU, as the brain of the computer, truly determines the overall performance, especially for demanding tasks.
How do you prioritize which component to upgrade first when building or enhancing a PC? Is it based on specific tasks, budget constraints, or future-proofing the system? I’d love to hear your thoughts on balancing these factors for an optimal setup!
This is a really insightful breakdown of computer components and their roles in a system. I particularly liked how you explained the importance of the motherboard as the central hub—it’s often overlooked when discussing PC builds. The comparison between SSDs and HDDs was well put, especially highlighting the trade-off between speed and cost. It’s interesting how much RAM can impact multitasking; I’ve experienced that firsthand! I’m curious, though, how do you recommend balancing the budget when building a PC? Should someone prioritize CPU over GPU, or vice versa, depending on their needs? Also, do you think AMD or Intel has an edge in 2023, or is it purely situational? Would love to hear your thoughts!
The motherboard is indeed the backbone of any computer, connecting all the essential components seamlessly. It’s fascinating how it dictates the compatibility of CPUs and RAM, ensuring everything works in harmony. RAM’s role in multitasking is crucial—more RAM means smoother performance, which is a game-changer for heavy users. The PSU is often overlooked, but as you mentioned, it’s the lifeline of the system; without it, nothing functions. SSDs versus HDDs is always an interesting debate—speed versus storage capacity, depending on individual needs. The CPU, being the brain, truly defines the system’s performance, especially for demanding tasks like gaming or editing. Do you think future advancements in CPU technology will eventually make HDDs obsolete, or will they still have a place in budget builds?
This is a really informative read! I never fully appreciated how crucial the motherboard is in connecting all the components and enabling communication. It’s fascinating how the choice of motherboard can dictate what kind of CPU and RAM you can use. I’ve always wondered if there’s a noticeable difference in performance between HDDs and SSDs for everyday tasks like web browsing or document editing. Also, how do you determine the right amount of RAM needed for multitasking without overdoing it? I’m considering upgrading my PC, and I’m torn between investing in a high-end CPU or prioritizing a larger SSD. What would you recommend for someone who primarily uses their computer for gaming and streaming? I’d love to hear your thoughts!
This is a very informative and well-structured explanation of the key components of a computer. I appreciate how it breaks down the roles of the motherboard, RAM, PSU, CPU, and storage options in a clear and concise manner. The comparison between SSDs and HDDs is particularly useful for someone trying to decide which storage option best suits their needs. I also like how it emphasizes the importance of choosing the right CPU based on core count, clock speed, and compatibility. However, I wonder if there’s a specific scenario where an HDD might still be a better choice over an SSD despite the speed difference? What’s your take on balancing cost and performance when building a PC? Would love to hear your thoughts!
This is a very informative breakdown of the key components of a computer and their roles. I found the explanation of the motherboard particularly interesting—it’s fascinating how it acts as the central hub connecting everything. The comparison between SSDs and HDDs is also helpful, especially for someone like me who’s trying to decide which one to go for. I’m curious, though, how much of a difference does the CPU’s core count really make for everyday tasks like browsing or office work? Also, do you think it’s worth investing in a high-end PSU if I’m not planning to overclock or use power-hungry components? Overall, this is a great guide for anyone looking to build or upgrade their PC, but I’d love to hear more about balancing cost and performance for a mid-range setup. What would you recommend for someone on a budget who still wants a decent gaming experience?
Processing is the central focus of the computer that serves as the driving force behind the system. The drive connects all components and allows for communication between them. The motherboard states what components (CPUs, RAM, etc.) can be implemented in the system. Another significant component is random access memory (RAM), which functions as short-term memory that the CPU can access. Higher RAM levels mean that the computer does not freeze or slow down when multitasking because there’s more information accessible for temporary file storage.The component that supplies power to every part of the unit is the power supply unit (PSU); getting an adequate PSU that offers sufficient power is crucial because without it, no other component can boot on. For storage, the components can be solid state drives (SSD) or hard disk drives (HDD); SSDs have faster read-write speeds meaning data access is faster—leading to a more responsive experience—while HDDs tend to be less expensive for larger storage sizes.Overall, knowing about these components aids in the decision-making process for implementing a well-balanced and efficient PC.The Central Processing Unit (CPU), often called the brain of the computer, orchestrates all instructions, powering exceptional system performance. A robust CPU delivers lightning-fast processing, seamless multitability, and flawless performance for intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, and complex data analysis. When selecting a CPU, prioritize key factors such as core count, clock speed, and motherboard compatibility to match your needs. Leading brands like Intel and AMD provide diverse options, from cost-effective processors to cutting-edge, high-performance models. Choosing the right CPU guarantees a smooth, responsive, and highly efficient computing experience tailored to your goals.When deciding between an SSD (Solid State Drive) and an HDD (Hard Disk Drive), it’s essential to consider speed, durability, and cost. SSDs use flash memory, offering significantly faster read-write speeds, making them ideal for faster data access and a more responsive experience. In contrast, HDDs are less expensive and often provide larger storage sizes, making them suitable for users who need abundant storage without frequent data access.
The motherboard is indeed the backbone of any computer, connecting all essential components seamlessly. It’s fascinating how it dictates the compatibility of CPUs and RAM, ensuring the system runs efficiently. RAM’s role in multitasking is crucial—more RAM means smoother performance, especially when handling multiple tasks. The PSU’s importance cannot be overstated; without it, the entire system would be lifeless. SSDs have revolutionized data access speeds, while HDDs remain a cost-effective solution for larger storage needs. Understanding these components is key to building a balanced and efficient PC.
What are your thoughts on the trade-off between SSD speed and HDD storage capacity—which do you prioritize and why?
This is a really insightful breakdown of computer components! I’ve always wondered how the motherboard ties everything together, and now it makes so much sense. The comparison between SSDs and HDDs is spot on—speed vs. storage capacity is such a tough choice. I’m curious, though, how do you decide on the right balance between CPU power and RAM for specific tasks like gaming or video editing? Also, do you think investing in a high-end PSU is worth it for a mid-range build? I’d love to hear your thoughts on whether prioritizing one component over another can make or break the overall performance. What’s your take on future-proofing a PC—should we always aim for the latest tech, or is it better to upgrade gradually?
Interesting read! I’ve always wondered how the motherboard acts as the central hub for all components—it’s fascinating how it dictates compatibility for CPUs and RAM. The comparison between SSDs and HDDs is spot on; speed versus cost is always a tough call. I’m curious, though, how much of a difference does RAM really make in everyday tasks? I’ve heard conflicting opinions. Also, when it comes to PSUs, is it better to go for a higher wattage than needed, or is that just overkill? And for CPUs, do you think the brand (Intel vs. AMD) really matters, or is it more about the specs? Would love to hear your thoughts!